Powder Processing Techniques
Powder processing techniques are the backbone of material transformation in powder technology. From mixing and granulation to compaction and spray-drying, this section explores the methods and machinery that ensure efficiency, precision, and quality in handling powders. Discover how these techniques optimize material properties to meet diverse industrial requirements.
Page menu
Featured Powder Processing Techniques articles
News And Articles In Your Inbox
Sign up and receive PowderTechnology.info news, articles, and content from our partners in a quick and easy monthly newsletter.

Powder Processing Techniques: Mixing and Blending
Mixing and blending are fundamental processes in powder technology, ensuring uniform distribution of components to achieve consistent product quality. Whether combining powders, incorporating additives, or preparing materials for downstream processes, precision and efficiency are critical. Explore various mixing techniques, including ribbon, paddle, and high-shear mixers, each tailored to specific material behaviors and production needs. Proper blending minimizes segregation, enhances homogeneity, and optimizes material performance for diverse industrial applications.
Featured Powder Mixing and Blending articles
More Mixing Articles
More Mixing Articles
Powder Processing Techniques: Granulation and Agglomeration
Granulation is a vital process in powder technology, transforming fine powders into larger, more cohesive granules. This improves flowability, reduces dustiness, and enhances handling properties. Techniques such as wet granulation, fluidized bed granulation, and melt granulation are tailored to specific material requirements and applications. Granules created through this process find extensive use in pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, and food industries, where uniform size, density, and performance are critical. Proper control of parameters ensures consistent quality and optimizes downstream processes.

More Granulation Articles
Featured Granulation and Agglomeration articles
More Granulation Articles

Powder Processing Techniques: Spray-Drying
Spray-drying is a highly efficient technique for converting liquid solutions or suspensions into fine, dry powders. This process uses atomization and rapid drying to create uniform particles with controlled size and moisture content. Widely used in food, pharmaceuticals, and ceramics, spray-drying ensures precision and scalability. By optimizing parameters like nozzle type, temperature, and airflow, manufacturers can produce powders with tailored properties to meet diverse application demands.
Featured Spray-Drying articles
More Spray-Drying Articles
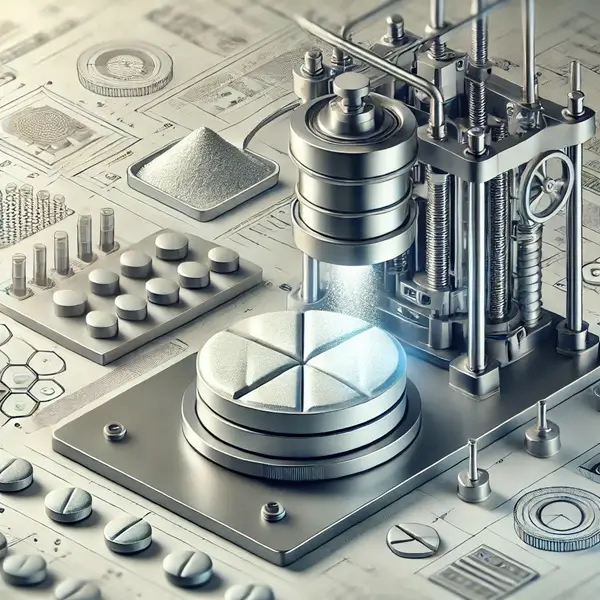
Powder Processing Techniques: Compaction
Compaction transforms powders into solid forms, enhancing material stability and usability. This process applies pressure to powders, creating compressed shapes such as tablets, pellets, or briquettes. Equipment like roller compactors and tableting presses ensure uniformity and density, tailored to specific material properties. Compaction improves handling, reduces storage volume, and meets functional requirements, making it indispensable in industries such as pharmaceuticals, metallurgy, and construction.

More Compaction Articles
Featured Compaction articles
More Compaction Articles

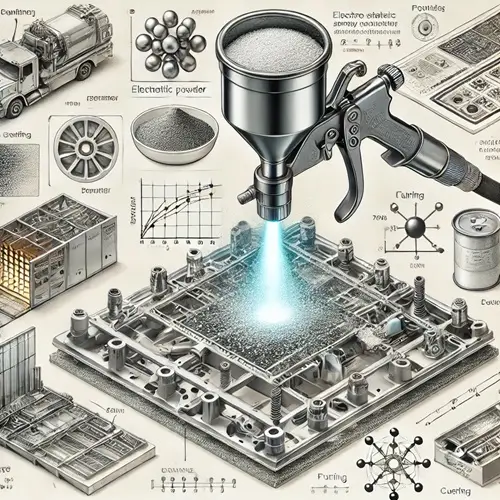
Powder Processing Techniques: Coating Processes
Coating processes play a crucial role in modifying the surface properties of particles to enhance functionality, durability, or aesthetic appeal. This involves applying a uniform layer to powders using techniques such as drum coaters or fluidized bed systems. Coating can improve flowability, protect against environmental factors, or impart desired chemical or physical properties. Achieving a consistent and precise coating is essential for ensuring performance and meeting industry standards in applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to advanced materials.