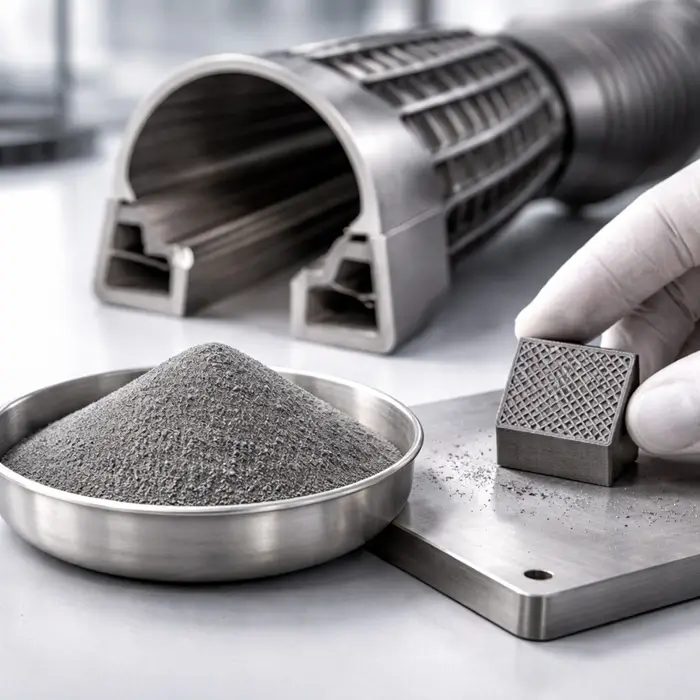
Powder Technology Insights
Powdertechnology.info
The Independent Knowledge Hub for Powder Processing
Expert insights, practical solutions, and industry developments.
All in one place.
All in one place.
Sign up for our Newsletter and be informed
Sign up for our Newsletter and be informed
Our Cornerstone Essential Guides
Featured Article
More Featured Articles
Industry knowledge
Case Studies
Industry Reports
Sustainibility Articles
Advertisement
Powder Technology Industries & Resources
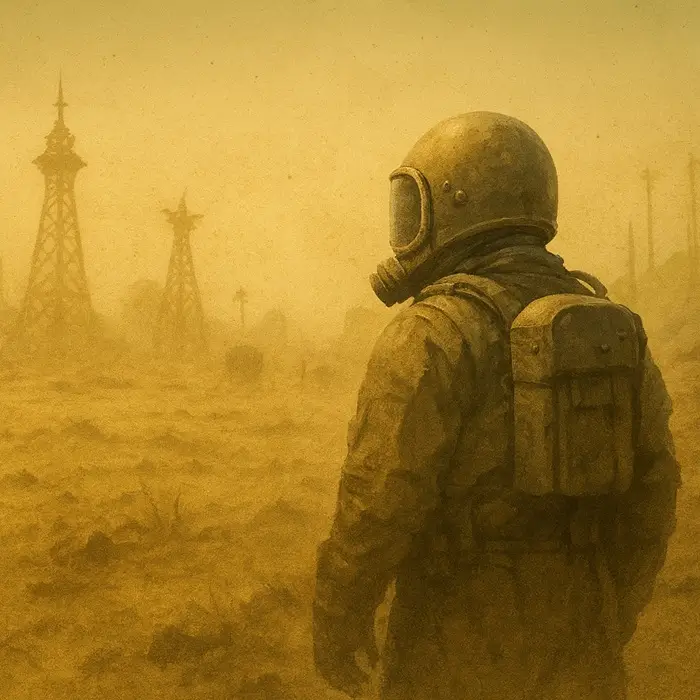
Powder Technology Insights: Science behind the fiction
Fallout’s wasteland: seen through a powder lens
Fallout’s wasteland feels grounded because it treats dust as an ever-present danger. Real nuclear fallout behaves differently, but the core idea is rooted in realism. Radioactive particles circulate through the air, settle in patches, stick to surfaces, and keep returning as dust for decades. Table of contents If you play the game or watch the show, the Fallout wasteland feels strangely believable. [...]